Hello folks, Today I'll be sharing some insights and overview of a very naïve classification model in machine learning named K-Nearest Neighbors Classifier a.k.a KNNClassifier.
It is a supervised learning algorithm used for Classification and Regression as well. However we will limit the discussion to Classification in this post.
To use the K-Nearest Neighbours Classifier we import the KNeighborsClassifier from sklearn module using the code below.
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
You can find the official documentation link below for further insight and deeper dive. KNeighborsClassifier
This classifier is based on the principle of calculating the number of nearest points to the given test sample and then assigns the classes to the sample that the model feels it suits best.
We create the classifier and then fit the training data on the classifier as shown below...
knn = KNeighborsClassifier()
knn.fit(X_train, y_train)
An example of a classifier that classifies various fruits is shown below along the decision boundaries and the corresponding regions.
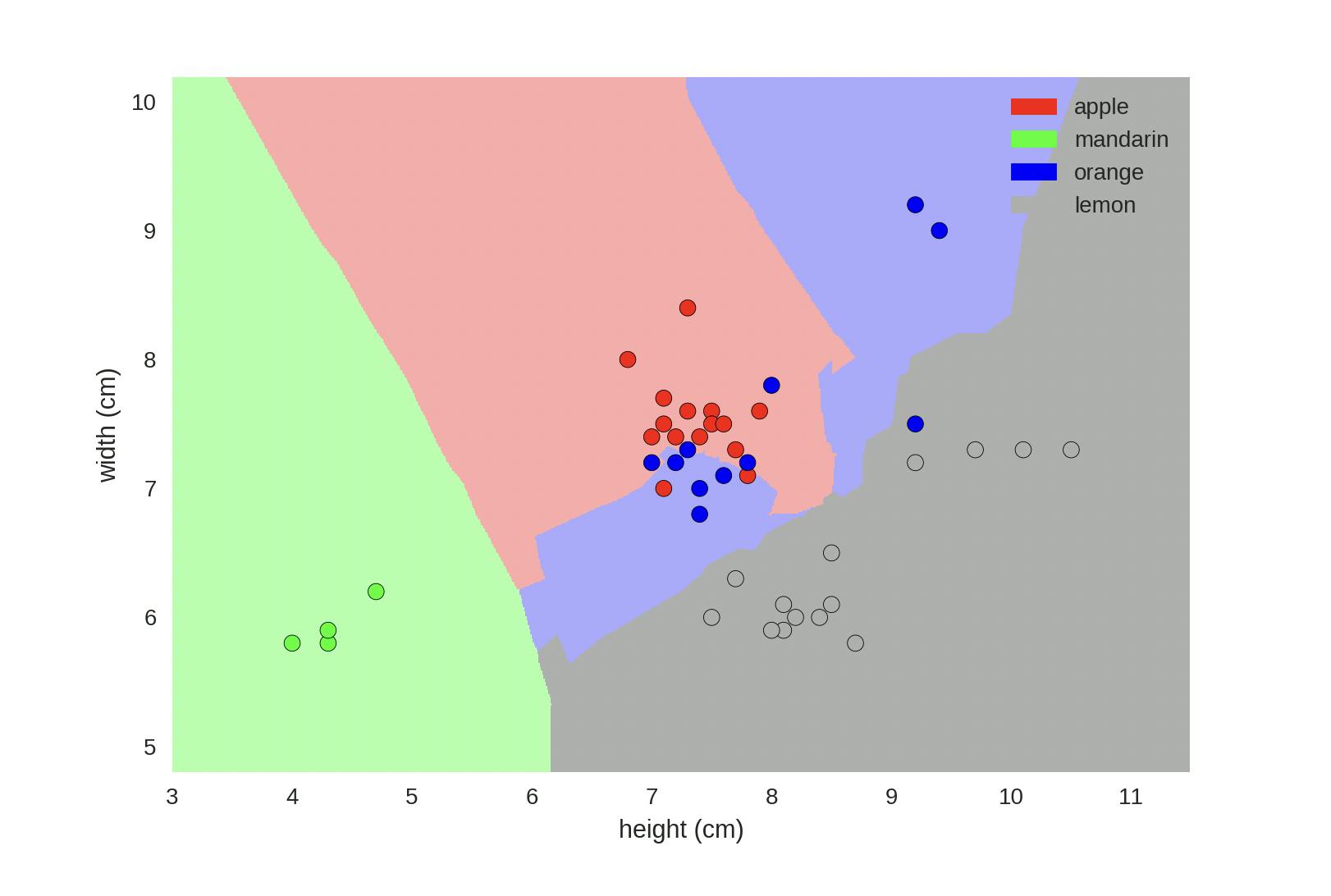
Parameters
Like many other machine learning models, the KNeighborsClassifier has its set of parameters to tweak to create a good fit for the training data. We will not be discussing about all the parameters, but few of them are explained below...
n_neighbors : int, default=5 -> The number of points in the training set that the new test sample must be calculated to be nearest.
weights : {‘uniform’, ‘distance’} or callable, default=’uniform’ -> Assign weights to the points based on distance or treat all points with equal weights.
metric : str or callable, default=’minkowski’ -> The method to calculate the distance between 2 points. The default parameter 'minkowski' calculates the Euclidean distance between the 2 points. There are few other minor parameters and some attributes that we won't be discussing here. Feel free to refer to the documentation if you need more insight.
Below is shown to create a model using custom parameters.
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=10, weights='uniform').fit(X_train, y_train)
Choosing the most important parameter : 'K'
Choosing a value for 'K' is the most important task of training a KNeighborsClassifier. (Although the appropriate value of K entirely depends on the input data).
Typically a lower value of 'K' tends to overfit to the training data and may result in excellent training accuracy but scores low on the test set accuracy. This happens to due to complex decision boundaries associated with the training data.
A higher value of 'K' might to simpler decision boundaries that cannot score well neither on the training data nor the test data as a result of underfitting to the training data.
An intermediate value of 'K' might lead to a perfect fit scoring well on the training data as well as the test data though the perfect value of 'K' needs some thorough exploration.
Shown below are some images with the decision boundaries of KNN Classifier varying on the parameter 'K'. Also we can see how the training_set accuracy and test_set accuracy vary with varying 'K'.
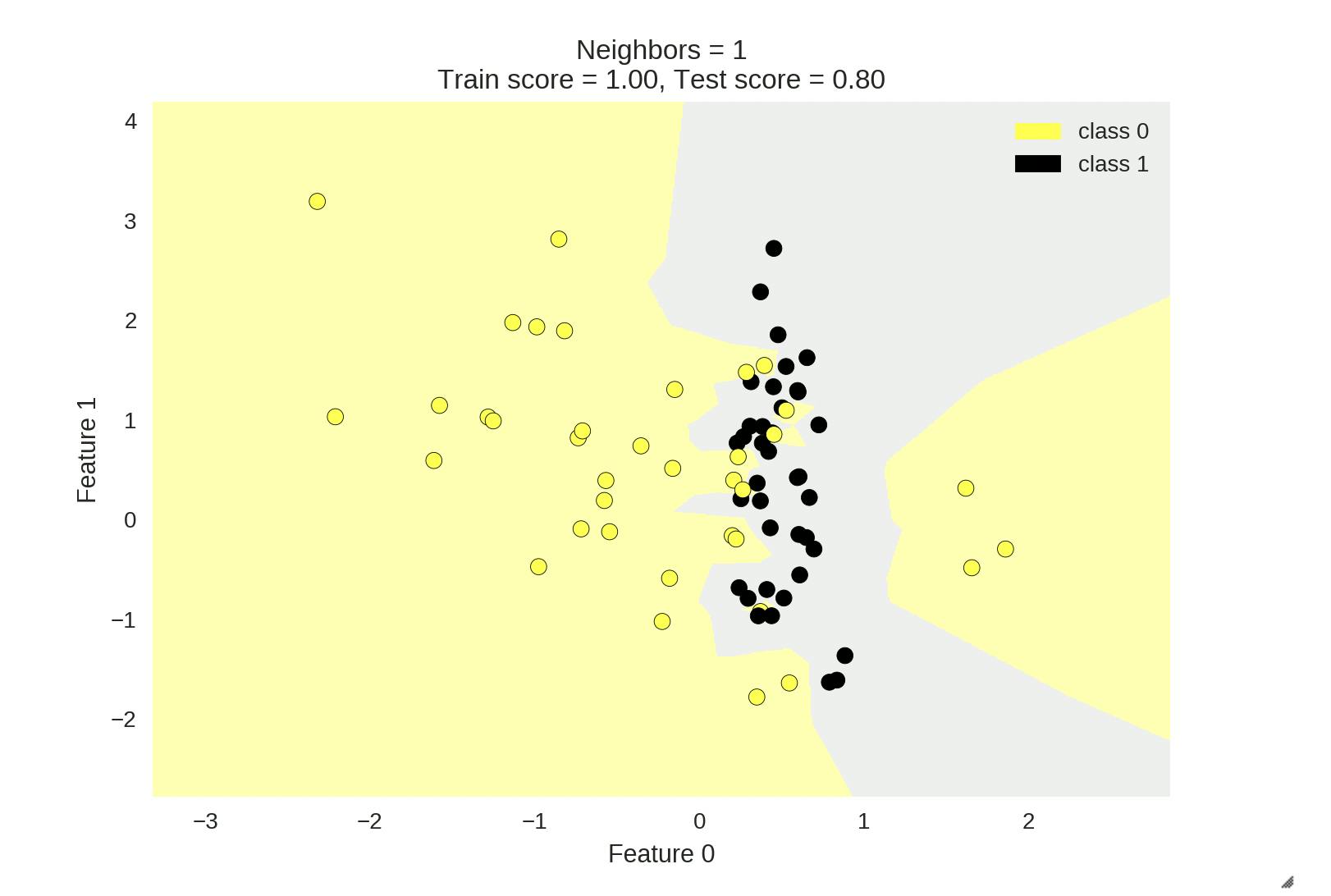
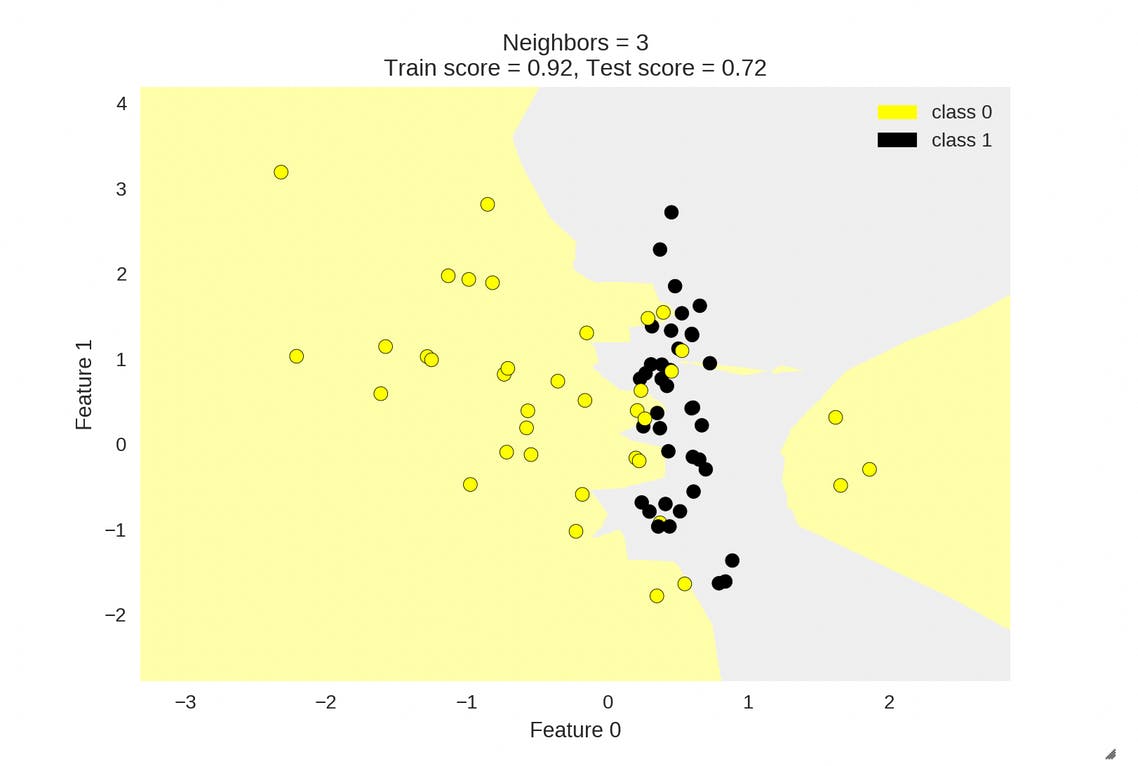
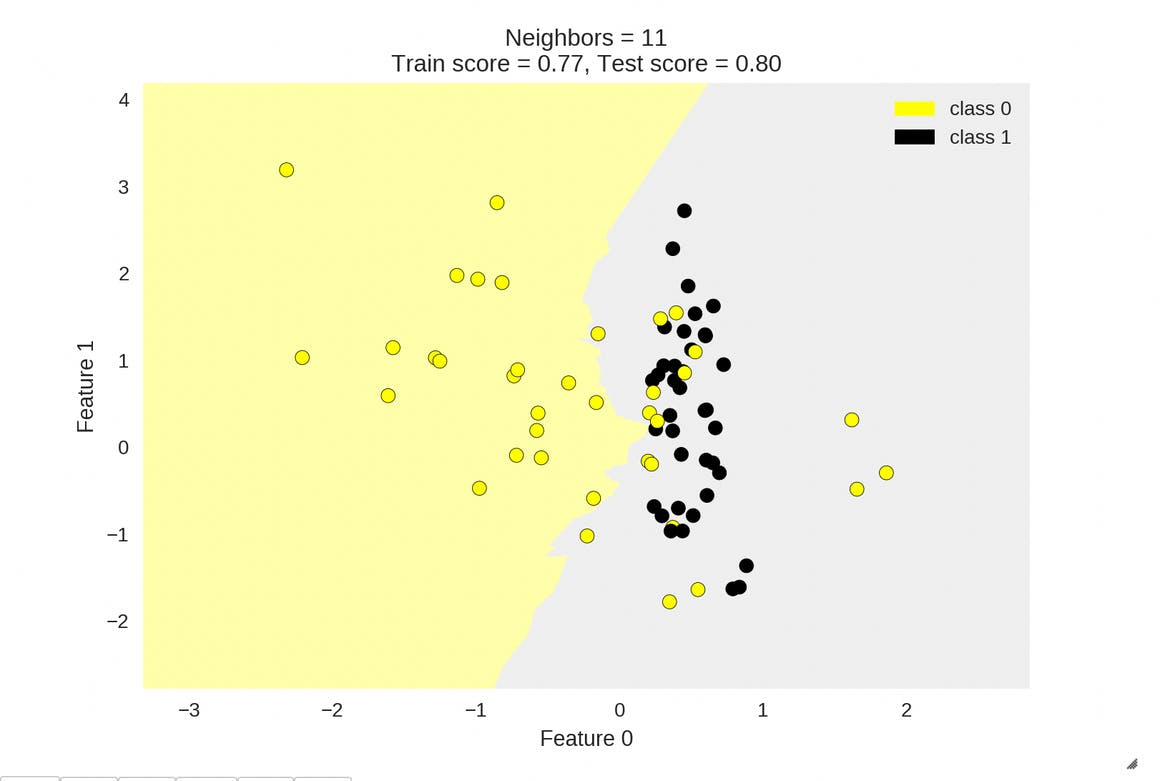
Feature Preprocessing
Typically the values of the input features have different boundaries. However it is ideal to scale all the input features so that they lie in the same scale. This is done using the sklearn.preprocessing.MinMaxScaler class as show below.
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
X_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
knn.fit(X_train, y_train)
We are not going to discuss in detail the functioning of MinMaxScaler but what is essentially does is convert all input feature values to range between [0, 1].
The formula to perform the transformation is given below.
$$ x' = \frac{(x - x_{min})} {x_{max} - x_{min}} * (max - min) + min $$
where \(x_{min}\) represents minimum value in the column, \(x_{max}\) represents maximum value in the column, \(x'\) represents scaled/transformed value and \(x\) represents the actual value of x. \(min\) and \(max\) respectively represent the minimum and maximum values of the scaled range.
X_std = (X - X.min(axis=0)) / (X.max(axis=0) - X.min(axis=0))
X_scaled = X_std * (max - min) + min
Feel free to refer to the official documentation at the link provided below for further insight.
Pros And Cons

Pros
A very simple and easy to interpret and understand yet powerful classifier for certain datasets.
Can be used as a baseline to compare against a more complex classifiers.
Not much parameter tuning is required.
Cons
Cannot be efficiently used for large datasets or even datasets with large number of features as it is required to memorise all of the training instances.
Not so powerful classifier that can be applied to all datasets.
And that's a wrap up folks. Please like this post if you found it insightful, share it others who would appreciate it!! Comments and Suggestions will be greatly appreciated. Thanks for reading, have a wonderful day! 😁
